Introduction
This tutorial is a simplified introduction to:
tidyversePackage- Data Download within R
- Data Cleaning & Wrangling
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- The goal of EDA is to uncover insights, and check assumptions about the data.
- We achieve this by visualising and applying statistical techniques on the data.
Installation
The code below installs a set of R packages.
# Package names
packages <- c( "tidyverse" )
# Install uninstalled packages
installed_packages <- packages %in% rownames( installed.packages() )
if ( any(installed_packages == FALSE) ) {
install.packages( packages[!installed_packages] )
} else {
cat("The package(s) is/are already installed!\n")
}
What the script does?
- First, the code creates a vector called
packageswhich only contains thetidyversepackage name. - Then, the code checks if the
tidyversepackage is already installed by checking if the package name is present in the rownames of theinstalled.packages()object. The result of this check is stored in theinstalled_packagesobject.
A. If thetidyversepackage is not installed, the code uses theinstall.packages()function to install the package.
B. If the package is already installed, the code outputs a message indicating that the package is already installed. - The code uses the
anyfunction to check if there are any uninstalled packages in thepackagesvector. - And, the
catfunction to print out a message indicating the status of the package installation.
## The package(s) is/are already installed!
Loading packages
# Loading packages
invisible( lapply(packages, library, character.only = TRUE) )
## ── Attaching packages ────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.2 ── ## ✔ ggplot2 3.4.1 ✔ purrr 1.0.1 ## ✔ tibble 3.1.8 ✔ dplyr 1.1.0 ## ✔ tidyr 1.3.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.0 ## ✔ readr 2.1.4 ✔ forcats 1.0.0 ## ── Conflicts ───────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ── ## ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter() ## ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
The library(tidyverse) will load the core tidyverse packages:
ggplot2for data visualisationdplyrfor data manipulationtidyrfor data tidyingreadrfor data importpurrrfor functional programmingtibblefor tibbles, a modern re-imagining of data framesstringrfor stringsforcatsfor factors
Data Download
From the gapminder project, we obtain data for “GDP per capita”, “Life expectancy”, “Population”, and “Country codes”.
url <- "https://github.com/Gapminder/csv-conf-2017-talk/raw/master/data/ddf--bubbles-2/"
file1 <- "ddf--datapoints--gdp_per_capita--by--country--time.csv"
gdp_per_capita <- read_csv( paste0(url, file1) )
## Rows: 43639 Columns: 3 ## ── Column specification ─────────────────────────────────────────────── ## Delimiter: "," ## chr (1): country ## dbl (2): time, gdp_per_capita ## ## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
gdp_per_capita
## # A tibble: 43,639 × 3 ## country time gdp_per_capita ## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 afg 1800 603 ## 2 alb 1800 667 ## 3 dza 1800 716 ## 4 and 1800 1197 ## 5 ago 1800 618 ## 6 atg 1800 757 ## 7 arg 1800 1507 ## 8 arm 1800 514 ## 9 abw 1800 833 ## 10 aus 1800 815 ## # … with 43,629 more rows
file2 <- "ddf--datapoints--life_expectancy--by--country--time.csv"
life_expectancy <- read_csv(paste0(url, file2))
## Rows: 54787 Columns: 3 ## ── Column specification ─────────────────────────────────────────────── ## Delimiter: "," ## chr (1): country ## dbl (2): time, life_expectancy ## ## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
life_expectancy
## # A tibble: 54,787 × 3 ## country time life_expectancy ## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 afg 1800 28.2 ## 2 alb 1800 35.4 ## 3 dza 1800 28.8 ## 4 and 1800 NA ## 5 ago 1800 27.0 ## 6 atg 1800 33.5 ## 7 arg 1800 33.2 ## 8 arm 1800 34 ## 9 abw 1800 34.4 ## 10 aus 1800 34.0 ## # … with 54,777 more rows
file3 <- "ddf--datapoints--population--by--country--time.csv"
population <- read_csv( paste0(url, file3) )
## Rows: 54787 Columns: 3 ## ── Column specification ─────────────────────────────────────────────── ## Delimiter: "," ## chr (1): country ## dbl (2): time, population ## ## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
population
## # A tibble: 54,787 × 3 ## country time population ## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 afg 1800 3280000 ## 2 alb 1800 410445 ## 3 dza 1800 2503218 ## 4 and 1800 2654 ## 5 ago 1800 1567028 ## 6 atg 1800 37000 ## 7 arg 1800 534000 ## 8 arm 1800 413326 ## 9 abw 1800 19286 ## 10 aus 1800 351014 ## # … with 54,777 more rows
Data Cleaning
After reading the country_code in, the function “str_to_title” is used to convert all the values in the “world_4region” column to title case. In other words, it capitalizes the first letter of each word in the column.
file4 <- "ddf--entities--country.csv"
country_code <- read_csv( paste0(url, file4) )
## Rows: 273 Columns: 5 ## ── Column specification ─────────────────────────────────────────────── ## Delimiter: "," ## chr (3): country, name, world_4region ## dbl (2): latitude, longitude ## ## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
country_code$world_4region <- str_to_title( country_code$world_4region )
country_code
## # A tibble: 273 × 5 ## country name world_4region latitude longitude ## <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 abkh Abkhazia Europe NA NA ## 2 afg Afghanistan Asia 33 66 ## 3 akr_a_dhe Akrotiri and Dhekelia Europe NA NA ## 4 ala Åland Europe 60.2 20 ## 5 alb Albania Europe 41 20 ## 6 dza Algeria Africa 28 3 ## 7 asm American Samoa Asia -11.1 -171. ## 8 and Andorra Europe 42.5 1.52 ## 9 ago Angola Africa -12.5 18.5 ## 10 aia Anguilla Americas 18.2 -63.0 ## # … with 263 more rows
Combining the different tibbles and removing missing data.
country_code %>%
left_join( life_expectancy ) %>%
left_join( gdp_per_capita ) %>%
left_join( population ) %>%
select( name:population ) %>%
rename_at( vars(name, world_4region, time), ~ c("country", "continent", "year") ) %>%
drop_na() %>%
mutate( year = as.Date(paste(year, "-01-01", sep = "", format = "%Y-%b-%d"))) -> gapminder_df
## Joining with `by = join_by(country)`
## Warning in left_join(., life_expectancy): Each row in `x` is expected to match at most 1 row in `y`. ## ℹ Row 2 of `x` matches multiple rows. ## ℹ If multiple matches are expected, set `multiple = "all"` to silence ## this warning.
## Joining with `by = join_by(country, time)` ## Joining with `by = join_by(country, time)`
gapminder_df
## # A tibble: 41,124 × 8 ## country conti…¹ latit…² longi…³ year life_…⁴ gdp_p…⁵ popul…⁶ ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1800-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 2 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1801-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 3 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1802-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 4 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1803-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 5 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1804-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 6 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1805-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 7 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1806-01-01 28.2 603 3280000 ## 8 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1807-01-01 28.1 603 3280000 ## 9 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1808-01-01 28.1 603 3280000 ## 10 Afghanis… Asia 33 66 1809-01-01 28.1 603 3280000 ## # … with 41,114 more rows, and abbreviated variable names ¹continent, ## # ²latitude, ³longitude, ⁴life_expectancy, ⁵gdp_per_capita, ## # ⁶population
Data Wrangling
Checking data for the different continents. Here, Australia is categorised under Asia.
gapminder_df %>%
distinct( continent )
## # A tibble: 4 × 1 ## continent ## <chr> ## 1 Asia ## 2 Europe ## 3 Africa ## 4 Americas
gapminder_df %>% filter( grepl("[aA]ustralia", country) )
## # A tibble: 216 × 8 ## country conti…¹ latit…² longi…³ year life_…⁴ gdp_p…⁵ popul…⁶ ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 Australia Asia -25 135 1800-01-01 34.0 815 351014 ## 2 Australia Asia -25 135 1801-01-01 34.0 816 350143 ## 3 Australia Asia -25 135 1802-01-01 34.0 818 349274 ## 4 Australia Asia -25 135 1803-01-01 34.0 820 348407 ## 5 Australia Asia -25 135 1804-01-01 34.0 822 347543 ## 6 Australia Asia -25 135 1805-01-01 34.0 824 346681 ## 7 Australia Asia -25 135 1806-01-01 34.0 826 345821 ## 8 Australia Asia -25 135 1807-01-01 34.0 828 344963 ## 9 Australia Asia -25 135 1808-01-01 34.0 830 344107 ## 10 Australia Asia -25 135 1809-01-01 34.0 832 343253 ## # … with 206 more rows, and abbreviated variable names ¹continent, ## # ²latitude, ³longitude, ⁴life_expectancy, ⁵gdp_per_capita, ## # ⁶population
Reading in list of countries that are part of Oceania.
oceania <- read.csv( "oceania.csv", header = T ) # wikipedia
oceania
## V1 ## 1 Australia ## 2 New Zealand ## 3 Fiji ## 4 Papua New Guinea ## 5 Solomon Islands ## 6 Vanuatu ## 7 Federated States of Micronesia ## 8 Kiribati ## 9 Marshall Islands ## 10 Nauru ## 11 Palau ## 12 Samoa ## 13 Tonga ## 14 Tuvalu
sum( oceania$V1 %in% gapminder_df$country )
## [1] 10
In the code below, the if_else function is used to check if the values in the “country” column are present in the “V1” column of the “oceania” data frame. If the values are present, the “continent” column is updated with the value “Oceania”. If not, the original value in the “continent” column is kept unchanged.
gapminder_df %>%
mutate( continent = if_else(country %in% oceania$V1, "Oceania", continent) ) -> gapminder_df
gapminder_df %>% filter( grepl("[aA]ustralia", country) )
## # A tibble: 216 × 8 ## country conti…¹ latit…² longi…³ year life_…⁴ gdp_p…⁵ popul…⁶ ## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> ## 1 Australia Oceania -25 135 1800-01-01 34.0 815 351014 ## 2 Australia Oceania -25 135 1801-01-01 34.0 816 350143 ## 3 Australia Oceania -25 135 1802-01-01 34.0 818 349274 ## 4 Australia Oceania -25 135 1803-01-01 34.0 820 348407 ## 5 Australia Oceania -25 135 1804-01-01 34.0 822 347543 ## 6 Australia Oceania -25 135 1805-01-01 34.0 824 346681 ## 7 Australia Oceania -25 135 1806-01-01 34.0 826 345821 ## 8 Australia Oceania -25 135 1807-01-01 34.0 828 344963 ## 9 Australia Oceania -25 135 1808-01-01 34.0 830 344107 ## 10 Australia Oceania -25 135 1809-01-01 34.0 832 343253 ## # … with 206 more rows, and abbreviated variable names ¹continent, ## # ²latitude, ³longitude, ⁴life_expectancy, ⁵gdp_per_capita, ## # ⁶population
gapminder_df %>%
distinct( continent )
## # A tibble: 5 × 1 ## continent ## <chr> ## 1 Asia ## 2 Europe ## 3 Africa ## 4 Americas ## 5 Oceania
Data Analysis
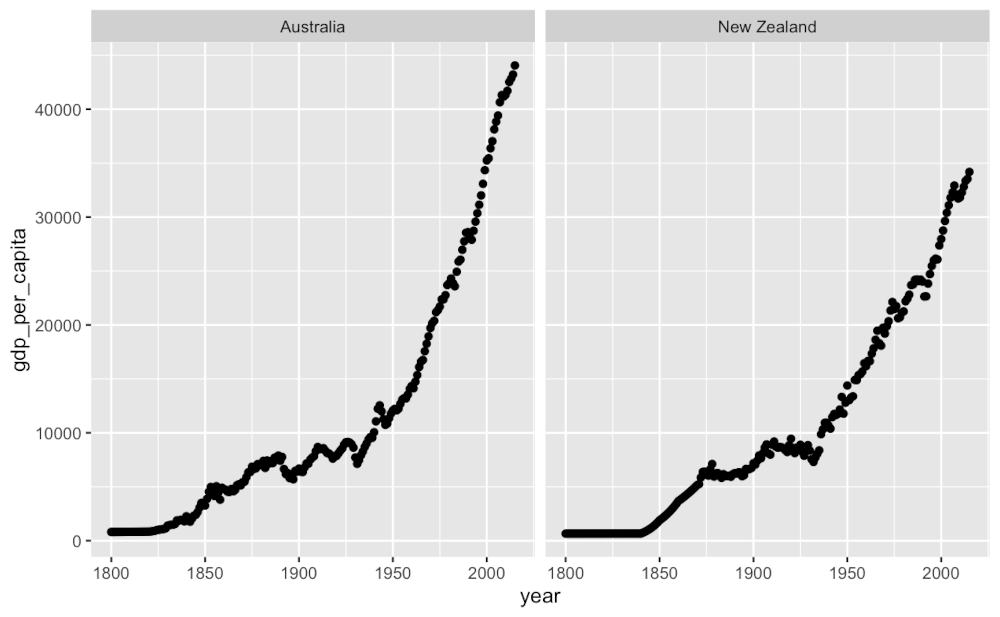
GDP Per Capita over the years (1800-2000)
gapminder_df %>%
filter( country == "New Zealand" | country == "Australia" ) %>%
# filter( continent == "Oceania" ) %>%
ggplot( aes(x = year, y = gdp_per_capita) ) +
geom_point() +
facet_wrap( . ~ country )
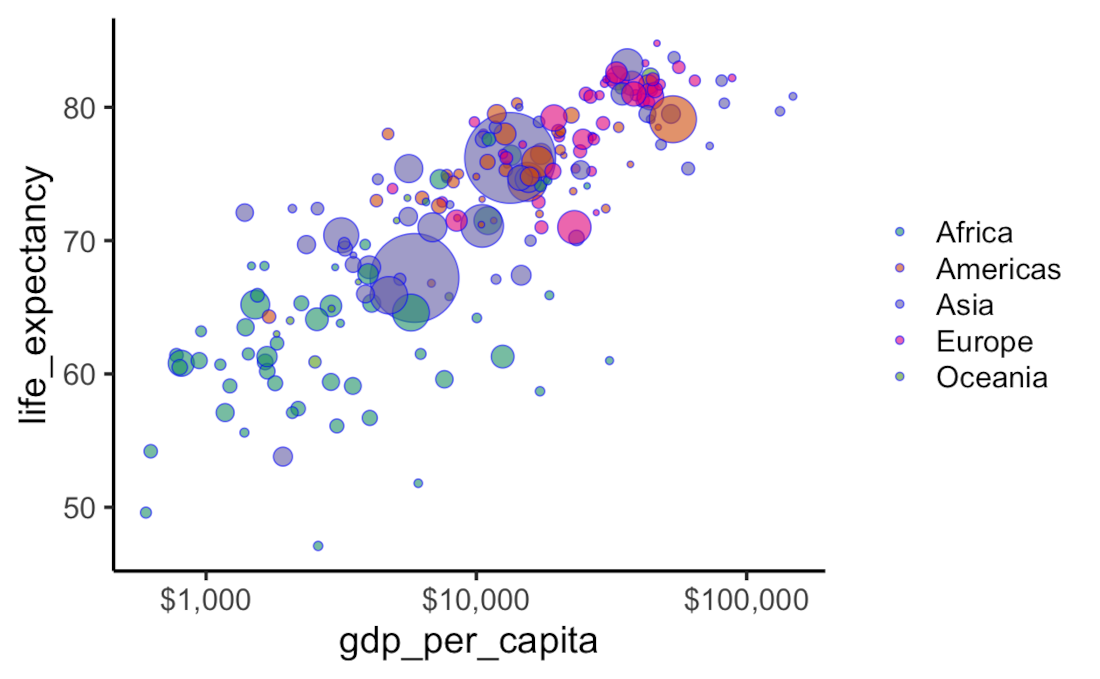
Life expectancy vs GDP Per Capita plot
gapminder_df %>%
filter( year == "2015-01-01" ) %>%
ggplot( aes(x = gdp_per_capita, y = life_expectancy) ) +
scale_x_log10(labels = scales::dollar) +
geom_point(aes(size = population, fill = continent), shape = 21, colour = "blue", alpha = 0.6) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Dark2") +
scale_size_continuous(range = c(1, 20)) +
guides(size = "none") +
theme_classic( base_size = 18 ) +
theme(panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
legend.position = "right",
legend.title = element_blank())
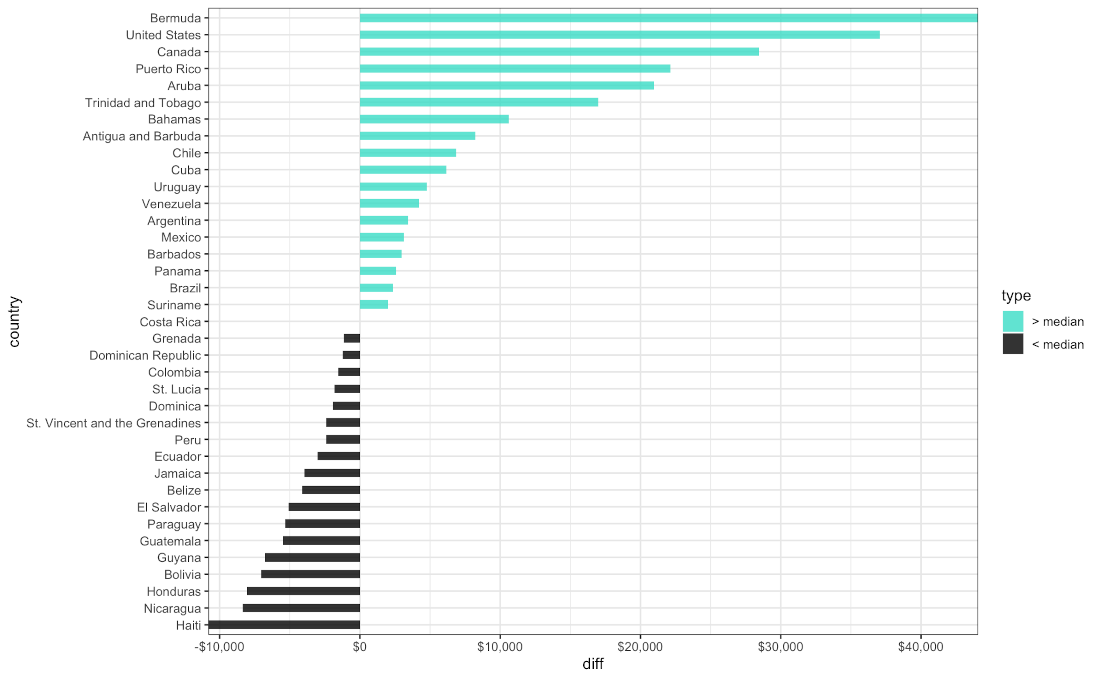
Difference in GDP per Capita for Countries in the Americas in 2015
gapminder_df %>%
filter(year == "2010-01-01" & continent == "Americas") %>%
mutate(median = median(gdp_per_capita),
diff = gdp_per_capita - median,
type = ifelse(gdp_per_capita < median, "Lower", "Higher")) %>%
arrange(diff) %>%
mutate(country = factor(country, levels = country)) %>%
ggplot( aes(x = country, y = diff, label = country) ) +
geom_col(aes(fill = type), width = 0.5, alpha = 0.8 ) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0),
labels = scales::dollar) +
scale_fill_manual(labels = c("> median", "< median"),
values = c("Higher" = "Turquoise", "Lower" = "black")) +
coord_flip() +
theme_bw( base_size = 12 )
sessionInfo()
## R version 4.2.1 (2022-06-23) ## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit) ## Running under: macOS Big Sur 11.7.3 ## ## Matrix products: default ## LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib ## ## locale: ## [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8 ## ## attached base packages: ## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods ## [7] base ## ## other attached packages: ## [1] forcats_1.0.0 stringr_1.5.0 dplyr_1.1.0 purrr_1.0.1 ## [5] readr_2.1.4 tidyr_1.3.0 tibble_3.1.8 ggplot2_3.4.1 ## [9] tidyverse_1.3.2 ## ## loaded via a namespace (and not attached): ## [1] lubridate_1.9.2 assertthat_0.2.1 digest_0.6.31 ## [4] utf8_1.2.3 R6_2.5.1 cellranger_1.1.0 ## [7] backports_1.4.1 reprex_2.0.2 evaluate_0.20 ## [10] highr_0.10 httr_1.4.4 pillar_1.8.1 ## [13] rlang_1.0.6 googlesheets4_1.0.1 curl_5.0.0 ## [16] readxl_1.4.2 rstudioapi_0.14 rmarkdown_2.21 ## [19] labeling_0.4.2 googledrive_2.0.0 bit_4.0.5 ## [22] munsell_0.5.0 broom_1.0.3 compiler_4.2.1 ## [25] modelr_0.1.10 xfun_0.38 pkgconfig_2.0.3 ## [28] htmltools_0.5.4 tidyselect_1.2.0 fansi_1.0.4 ## [31] crayon_1.5.2 tzdb_0.3.0 dbplyr_2.3.0 ## [34] withr_2.5.0 grid_4.2.1 jsonlite_1.8.4 ## [37] gtable_0.3.1 lifecycle_1.0.3 DBI_1.1.3 ## [40] magrittr_2.0.3 formatR_1.14 scales_1.2.1 ## [43] cli_3.6.0 stringi_1.7.12 vroom_1.6.1 ## [46] farver_2.1.1 fs_1.6.1 xml2_1.3.3 ## [49] ellipsis_0.3.2 generics_0.1.3 vctrs_0.5.2 ## [52] RColorBrewer_1.1-3 tools_4.2.1 bit64_4.0.5 ## [55] glue_1.6.2 markdown_1.5 hms_1.1.2 ## [58] parallel_4.2.1 fastmap_1.1.0 yaml_2.3.7 ## [61] timechange_0.2.0 colorspace_2.1-0 gargle_1.3.0 ## [64] rvest_1.0.3 knitr_1.42 haven_2.5.1
