Introduction
Python comes with built-in options for live coding and immediate execution, which include:
Python Shell
Python IDLE
Both options are available without any additional requirements other than Python installation.
| Python Shell | Python IDLE |
| is a built-in self-interpreter that can be activated directly in the terminal once Python is installed on a computing machine. This interpreter is also known as the REPL (Read-Evaluate-Print Loop). With Python shell you can write and execute Python code directly in a terminal. | is an integrated development environment (IDE) for Python that provides a more advanced coding environment than the Python shell. With Python IDLE, you can write, edit, and execute Python code in a single window (separated from the terminal window). |
You can easily start Python shell in a terminal using the python command (note: python3 for Python3). |
You can easily launch Python IDLE from a terminal using the idle command (note: idle3 for Python3). |
Here are some key differences between the Python Shell and IDLE:
| Python Shell | Python IDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| user interface | command-line interface | graphical user interface (GUI) with menus, toolbars, and other visual elements |
| fetures | basic features such as command history, tab completion, and syntax highlighting | advanced features such as code profiling, code coverage, and refactoring tools |
| workflow | designed for quick experimentation and testing | provides a more structured workflow for developing larger programs |
| difficulty | easy to use for a beginner and doesn’t require any setup | a great tool for more experienced Python developers |
If you’re just starting out with Python or working on small projects, the Python shell may be sufficient. However, if you’re working on larger projects or need more advanced features, IDLE or another Python IDE may be a better choice. For details, see Further Reading section in this tutorial.
First, install Python
To use Python Shell or IDLE, you first need to have Python installed on your computer. You can download the latest version of Python from the official Python website at https://www.python.org/downloads/ ⤴. Be sure to choose the version that is compatible with your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
Windows:
- Go to the official Python website at https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/ ⤴.
- Scroll down to the “Download Python” section and click on the button.
- Scroll down to the “Stable Releases” section and click on the latest version of Python.
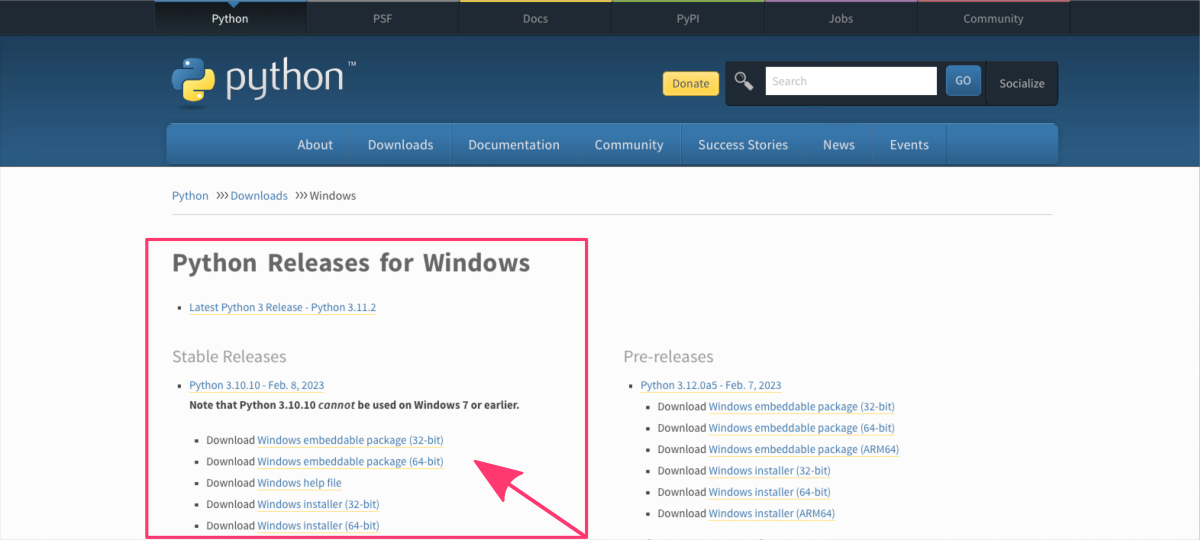
- Download the
"Windows x86-64 executable installer"for 64-bit Windows or
the"Windows x86 executable installer"for 32-bit Windows. - Run the installer and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation.
macOS:
A. MANUALLY
- Go to the official Python website at https://www.python.org/downloads/mac-osx/ ⤴.
- Scroll down to the “Download Python” section and click on the latest version of Python.
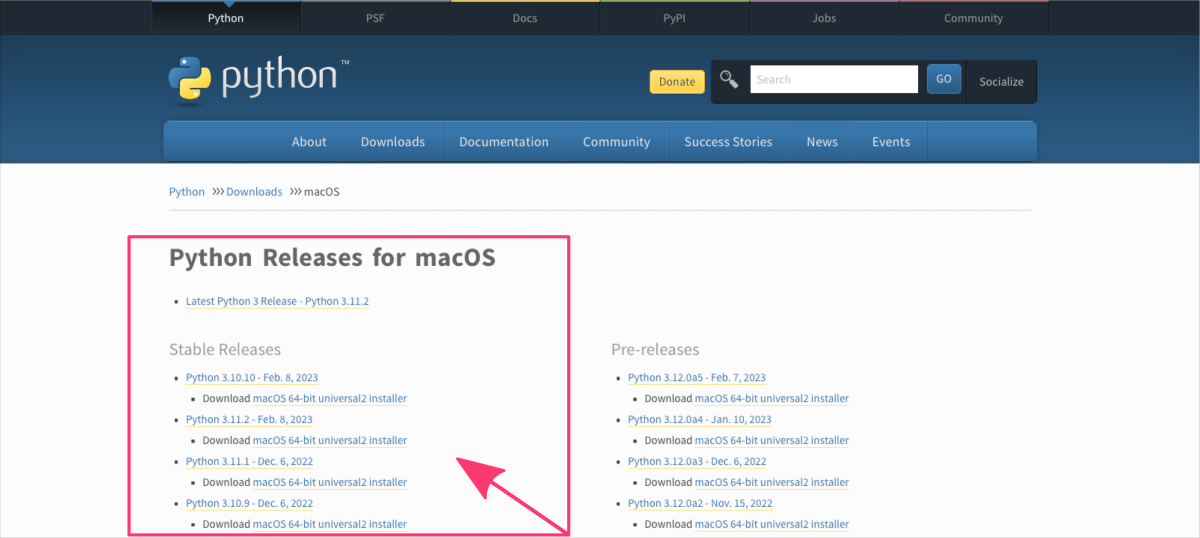
- Download the macOS installer package.
- Run the installer package and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation.
B. IN a TERMINAL
- Open the Terminal app on your Mac.
- First, check if you have Homebrew installed using the
brew -hcommand.
If you received an error message “Command not found”, then type the following command to install Homebrew (a package manager for macOS):/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)" - Wait for the installation to complete.
- Type the following command to install the latest release of Python:
brew install pythonand if you need a specific version of Python, provide it with the @ syntax:
brew install python@3.9
Linux (Ubuntu and Debian):
- Open a terminal window.
- Type the following command to install Python:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install python3
HPC system:
On a high-performance computing (HPC) system, it’s common to have multiple versions of Python pre-installed. This is because different software packages and applications may require different versions of Python or specific Python packages.
To switch between different versions of Python on an HPC system, you can use the module command. The module command allows you to load and unload software modules, including different versions of Python.
- Log in to the HPC system.
- Type the following command to see a list of available Python modules:
module avail python
[abadacz@nova23-1 ~]$ module avail python -------------- /opt/rit/el9/current/modules/lmod/linux-rhel9-x86_64/Core -------------- py-biopython/1.81-py310-wt5scj7 py-meson-python/0.13.1-py310-kvhvsds (D) py-gitpython/3.1.27-py310-pyitit6 py-python-dateutil/2.8.2-py39-rsw6pyr py-ipython-genutils/0.2.0-py310-bnwyyxn py-python-dateutil/2.8.2-py310-lnvzhiv (D) py-ipython/8.11.0-py310-lbl246q python/3.8.18-4j5jvxi py-meson-python/0.12.0-py310-kvp7vmw python/3.9.16-yukabfp py-meson-python/0.13.1-py39-py310-x75x5l2 python/3.10.10-zwlkg4l (D) py-meson-python/0.13.1-py310-cnxhztb r-findpython/1.0.7-py310-r42-a4fhsub Where: D: Default Module
- Look for the version of Python that you want to use.
The module name will typically include the version number, such aspython/3.9.16 - Type the following command to load the Python module:
module load python/3.9.16-yukabfp - Wait for the module to be loaded. This may take a few seconds.
[abadacz@nova23-1 ~]$ module load python/3.9.16-yukabfp
[abadacz@nova23-1 ~]$
- Type the following command to verify that the correct version of Python is being used:
python --versionThis should display the version number of the Python interpreter that you just loaded.
[abadacz@nova23-1 ~]$ python --version
Python 3.9.16
Once Python is installed on your computer, you can start using it to write and execute Python code.
See the following sections Python Shell and Python IDLE to get started with Python on your machine.
Python Shell
Python has a built-in shell with self-interpreter that can be activated directly in the terminal once Python is installed on a computing machine. It provides an interactive environment for executing Python commands by allowing the user to enter Python code one line at a time and immediately execute it to see the results of each command. The Python shell is useful for experimenting with Python syntax, performing quick calculations, and testing out small code snippets. It is a convenient way to quickly test out Python code and experiment with new ideas. It’s especially useful for beginners who are just learning Python and want to get a feel for how the language works.
Start a Python Shell
To start the Python shell, you need to have Python installed on your computer. If you haven’t already done so, go back to section First, install Python to make up for this step.
Once you have installed Python, you can start the Python shell by following these steps:
-
Open the terminal or command prompt on your computer.
- Type
pythonorpython3, depending on your system’s configuration, and pressEnteron your keyboard.python3 -
The Python Shell will start and display a prompt (
>>>) where you can start entering Python commands.
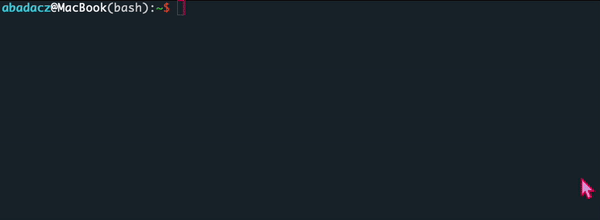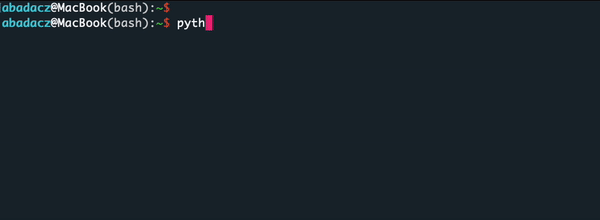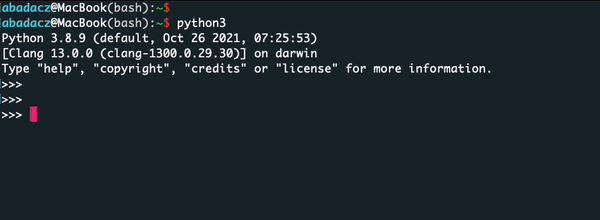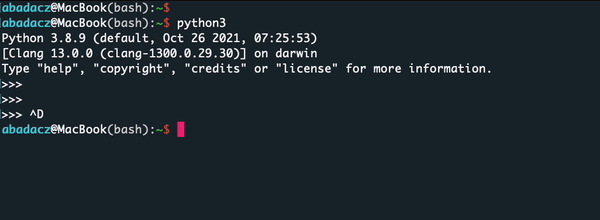
- Once the Python shell is running, you can write and execute Python code directly in the shell without the need to create script files. For example, you can use the shell to perform simple calculations, experiment with Python syntax, or test out small code snippets.
Let’s start with using the print()function to display the “Hello, world!” welcome messeage on the screen:print("Hello, world!")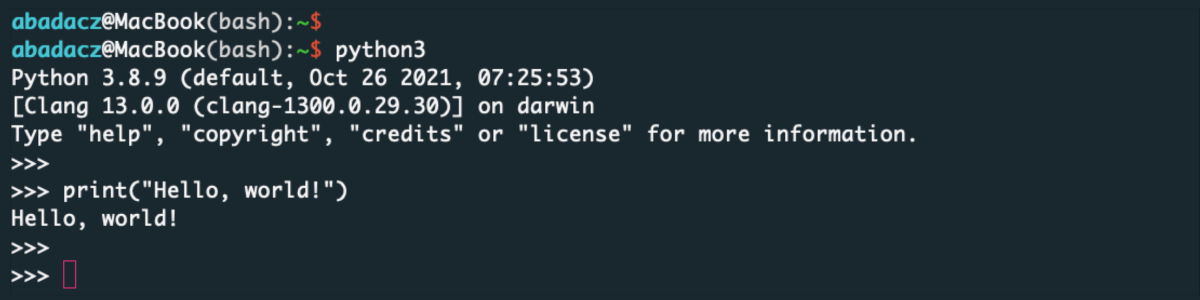 Now, you can try using the Python shell to perform a simple calculation:
Now, you can try using the Python shell to perform a simple calculation:a = 10 b = 5 c = a + b print(c)In this example, we created three variables (a, b, c) in the Python shell and assigned the values using the
=operator. We then used the+operator to add a and b together and assigned the result to the variable c. Finally, we printed the value of c to the console using theprint()function. - To terminate the Python shell press
CTRL + Dor typeexit()orquit()at the prompt and press Enter. You will automatically return to your basic shell (e.g., Bash).
>>> exit() abadacz@MacBook(bash):~$
Python IDLE
Integrated Development and Learning Environment (IDLE) is the default Python environment that comes with the standard installation of Python. It is a simple and lightweight environment that provides basic features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging.
Python IDLE is a useful tool for learning and working with Python, supporting the user with:
-
interactive mode
Python IDLE allows you to run Python code interactively, which means you can enter code directly into the shell and see the results immediately. It can be very helpful when you’re learning how to coding in Python. -
code editor
Python IDLE also includes a code editor that allows you to write and edit Python code in a more structured way than in interactive mode. The editor provides features such as syntax highlighting, indentation, and auto-completion to make it easier to write and read the code. -
debugging
Python IDLE includes a debugger that allows you to step through your code line by line and inspect variables as you go. This can be very helpful when you’re trying to track down a bug or understand how your code is working. -
help and documentation
Python IDLE provides access to Python’s built-in help system, which allows you to look up information about Python functions, modules, and other features. This can be very helpful when you’re trying to learn how to use a new feature or library in Python.
If you’re just getting started with Python, I would encourage you to give Python IDLE a try before the more advanced IDEs and see how it can help you on your learning journey. Once you have Python installed on your local machine, you can use IDLE offline any time without further configuration.
Launch an IDLE
Python IDLE can be launched from the command line or from your computer’s applications menu. If you haven’t installed Python yet, go back to section First, install Python to make up for this step.
To launch the Python IDLE from the terminal window, you can follow these steps:
-
Open the terminal or command prompt on your computer.
-
Type
idleoridle3, depending on your system’s configuration, and pressEnter.
Start typingidle, then press theTABkey twice to display available IDLE variants.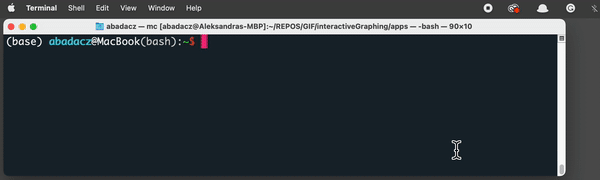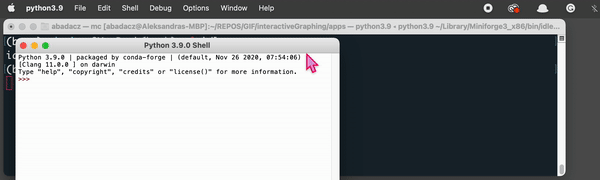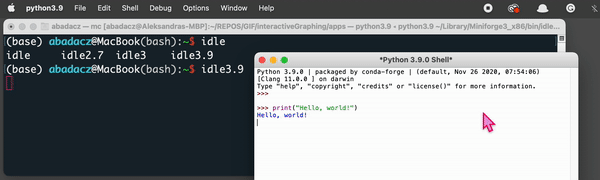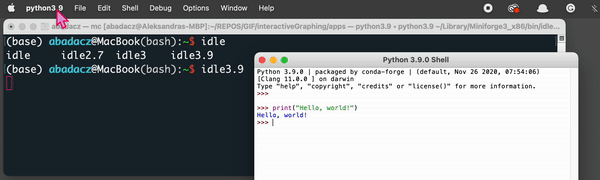
-
The Python IDLE will open in a separate window, providing you graphical user interface (GUI) with a on the top. By default, the first view in the IDLE is a Python Shell, which works the same as the interactive Python shell started directly in the terminal.
-
You can use the Python IDLE to create, edit, and run Python code.
- To create a new Python file in IDLE, click
File > New File, or pressCtrl+Non Windows orCommand+Non Mac.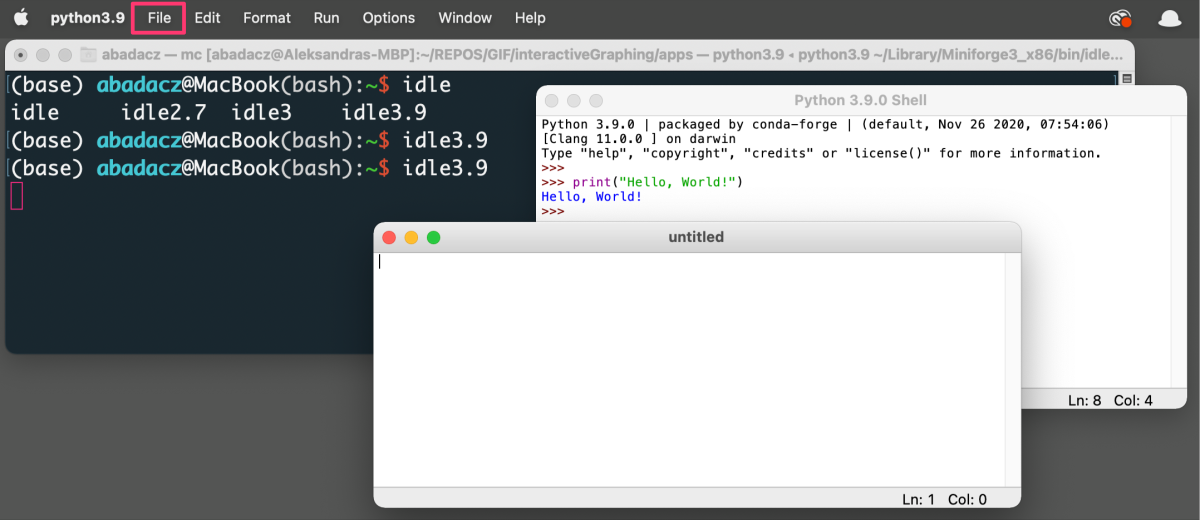
- To save your code, click
File > Save, or pressCtrl+Son Windows orCommand+Son Mac. You can customize the file name and saving location in the pop-up dialog box. - You can run code in IDLE by clicking
Run > Run Module, or pressingF5on the keyboard. The output will be displayed in the Python shell at the bottom of the IDLE window.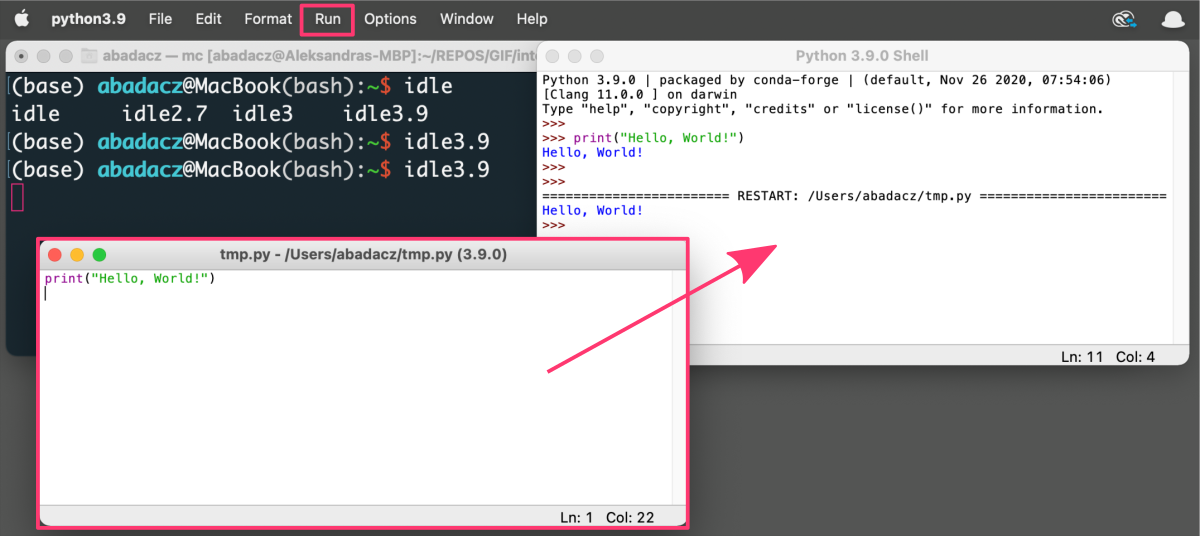
- To create a new Python file in IDLE, click
It is highly recommended to learn more about the basics of programming in Python by working through the hands-on tutorials provided in section 05. Introduction to Programming / Introduction to Python programming. These tutorials cover topics such as variables, data types, operators, control flow statements, functions, and more.
Further Reading
Text editors: create Python code in terminal text files (intermediate)Jupyter Lab: create an interactive Python notebook (advanced)
PyCharm: IDE for professional Python developers (professional)
R programming environment(s)
RStudio: integrated environment for R programming
Setting up RStudio
MODULE 05: Introduction to Programming
